US woman with rare double uterus gives birth to twin girls
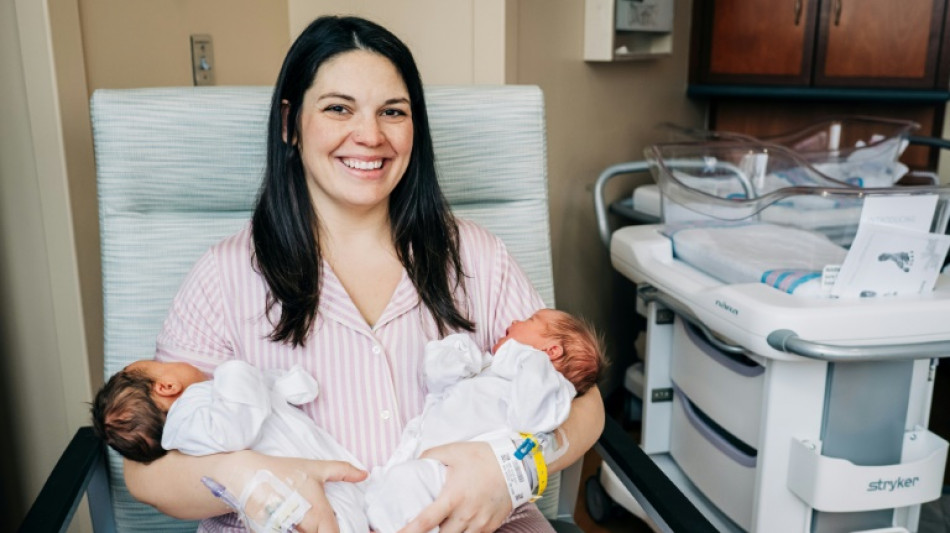
A 32-year-old woman from Alabama who was born with two uteruses and became pregnant in both gave birth to twin girls on different days, she announced on Friday.
"Our miracle babies were born!" Kelsey Hatcher, who is documenting her story on her Instagram account "doubleuhatchlings," wrote in a post.
She added that the girls "decided they were rare enough statistically that they should just go ahead and have their own birthdays too."
The first one, named Roxi Layla, was born on Tuesday at 7:49 pm (0149 GMT Wednesday). She was joined by Rebel Laken on Wednesday at 6:09 am. Each weighed over seven pounds (3.2 kilos).
Doctors had estimated a Christmas due date. But following 20 hours of combined labor after Hatcher was induced at 39 weeks, the sisters arrived just in time to be at home for the holidays with their siblings.
The mother and daughters have been discharged from the hospital, with Hatcher promising to share details about the delivery in future.
Hatcher knew from the age of 17 that she had "uterus didelphys," a rare congenital condition thought to affect about 0.3 percent of females. In such cases, each uterus has only one ovary and one fallopian tube.
It was during a routine eight-week ultrasound visit in May that Hatcher, a massage therapist and then-mother-of-three, learned not only that she was having twins this time, but that a fetus was present in each of her uteruses.
"As soon as she (the technician) moved the wand to the other uterus, I gasped," Kelsey recalled, according to a statement by University of Alabama at Birmingham Hospital.
"Sure enough, there was another baby. We just could not believe it."
Pregnancies in both uteruses are exceedingly rare, according to Shweta Patel, the obstetrician-gynecologist who cared for Hatcher at UAB's Women & Infants Center.
Patel was Hatcher's doctor during her third pregnancy. "But that was only one baby -- two babies in two uteri were a true medical surprise," she said in the statement, noting she received additional help from UAB experts in high-risk obstetrics.
Richard Davis, professor at the hospital's Division of Maternal-Fetal Medicine, said the congenital anomaly of Hatcher's dicavitary twin pregnancy meant her babies were not forced to share a single, cramped womb, a condition that would have made pre-term birth a high possibility.
"With Kelsey's babies, they each had their own womb, sac, placenta and umbilical cord, allowing them extra space to grow and develop," Davis said in the statement, which was accompanied by a hospital-produced video about Hatcher's pregnancy and delivery.
Hatcher said she was told the odds of a double pregnancy in double wombs were one in 50 million -- with the last widely known case in Bangladesh in 2019, when Arifa Sultana, then 20, gave birth to healthy babies 26 days apart.
Th.Frei--HHA